Slow WiFi can make even simple tasks—like watching a video or sending an email—feel painful. The good news: in many cases, you can speed things up without buying new equipment or calling your internet provider.
This guide walks you through easy, practical fixes you can try today to boost your WiFi speed at home.

1. Check Your Actual Internet Speed
Before changing anything, find out what you’re really getting.
- Stand near your router (same room).
- Turn off VPNs.
- Run a speed test on your phone or laptop using:
Compare the result with the speed you’re paying for in your internet plan.
- If the result is much lower even close to the router, the problem might be:
- Your internet provider
- Old modem/router
- If it’s good near the router but bad in other rooms, it’s likely:
- Weak WiFi signal
- Bad router placement
- Interference
Knowing this helps you fix the right problem.
2. Move Your Router to a Better Spot
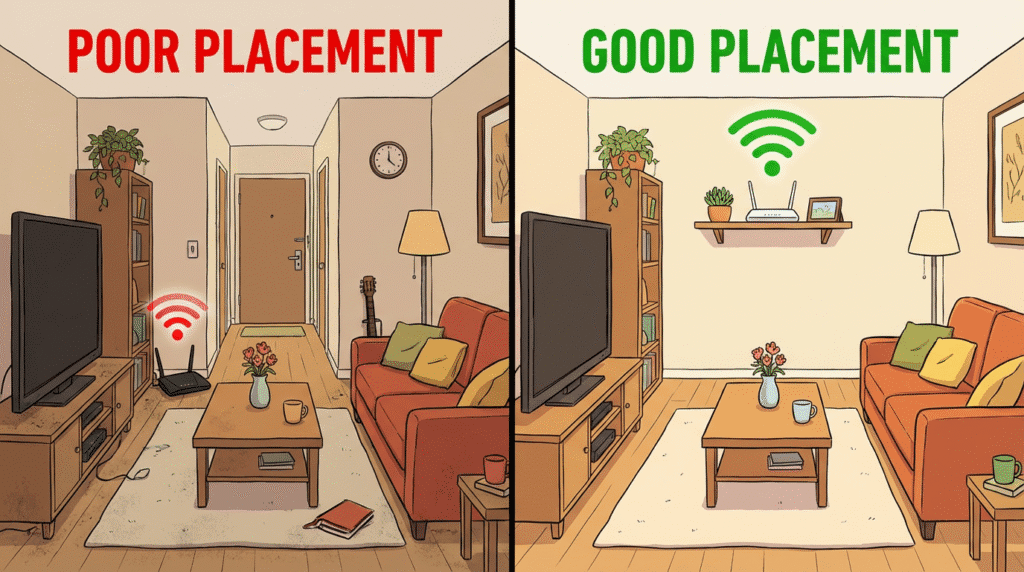
Router location can make a huge difference.
Best placement:
- As central in your home as possible
- High up (on a shelf, not on the floor)
- In an open area, not inside a cabinet
- Away from:
- Thick walls (brick, concrete)
- Metal stuff & devices Microwaves, cordless telephones, baby monitors
Avoid:
- Putting the router behind a TV
- Hiding it in a closed cupboard
- Leaving it on the floor in a corner Simply relocating your router to an open, more central location can significantly improve WiFi speed and coverage.
Just moving your router to a more open, central position can noticeably boost WiFi speed and coverage.
3. Choose the Right WiFi Band (2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz vs 6 GHz)

Here are the basics: Today’s routers typically have at least two WiFi bands:
- 2.4 GHz
- Slower, but longer range
- Best for phones, laptops and TVs close to the router
- 5 GHz
- Faster, but shorter range
- Best for phones, laptops, TVs near the router
- 6 GHz (Wi-Fi 6E, as long as your router supports it)
- Too early, too few in number, too limited range.
- Ideal for new devices tucked between heavy webs of communication.
What to do:
- Connect work devices, such as laptops, and smart TVs to the 5 GHz (or 6 GHz) network when it’s possible.
- For older devices and smart appliances, keep them on a 2.4 GHz network.
- If your router’s Wi-Fi networks use the name for both frequency bands your iOS/android device could connect to the 5 GHz network when you intend it to use the 2.4 GHz band.
- Log into your router settings
- Give each band a different name (e.g.,
HomeWiFi-2GandHomeWiFi-5G) - Manually choose the best one for each device
4. Reduce Interference from Other Networks
If you live in an apartment or dense area, nearby WiFi networks can interfere with yours.
Fixes:
- Change your WiFi channel
- Log into your router (typed on the bottom of the device, often something like
192.168.0.1or192.168.1.1). - Look for Wireless settings.
- For 2.4 GHz, try channels 1, 6, or 11.
- For 5 GHz, let the router select automatically or try a different channel if your interface allows.
- Log into your router (typed on the bottom of the device, often something like
- Turn off extra networks
- Disable any unused “Guest” networks or duplicate SSIDs you don’t need.
- This reduces congestion and confusion.
5. Update Your Router’s Firmware
Outdated router software can slow things down or cause random drops.
How to update:
- Log into your router’s admin page.
- Find Firmware Update, System, or Maintenance.
- Click Check for updates or follow the on-screen instructions.
- Let it restart if needed.
Do the same for your devices:
- Update your phone, laptop, and smart TV operating systems.
- Old software can also affect WiFi performance.
6. Secure Your WiFi Network
If neighbors or strangers are using your WiFi, your speed will suffer.
Steps:
- Make sure you’re using WPA2 or WPA3 security (not WEP or “Open”).
- Set a strong WiFi password:
- At least 12 characters
- Mix of letters, numbers, and symbols
- Change the default network name (SSID) so it doesn’t show your router brand and model.
- In your router’s admin page, check the connected devices list and remove or block any you don’t recognize.
Fewer unauthorized users = more bandwidth for you.
7. Limit Heavy Usage on Your Network
Streaming, gaming, large downloads, and video calls all use a lot of bandwidth.
Practical tips:
- Avoid multiple 4K streams at the same time.
- Lower video quality to 1080p or 720p on streaming apps when possible.
- Schedule large downloads or backups for night-time or when nobody’s working/streaming.
- Ask family members to pause downloads or updates during important meetings or calls.
If you have a big household, consider upgrading to a higher-speed plan if everyone is online at once.
8. Use Quality of Service (QoS) to Prioritize Important Traffic
Many modern routers include QoS (Quality of Service) or Traffic Priority settings.
QoS lets you:
- Give priority to certain devices (e.g., your work laptop)
- Or prioritize certain activity types (e.g., video calls, conferencing apps)
How to use QoS (general idea):
- Log into your router settings.
- Look for QoS, Traffic Control, or Bandwidth Control.
- Choose:
- Device-based priority (select your laptop or work PC)
- Or service-based (e.g., Zoom, Teams, Google Meet)
- Save and reboot the router if needed.
This doesn’t increase your total speed, but it makes critical tasks feel much smoother.
9. Consider a WiFi Extender or Mesh System
If your speed is fine near the router but bad in other rooms, your signal just isn’t reaching far enough.
You have two common options:
WiFi Extender (Repeater)
- Cheaper
- Plugs into a power socket between your router and weak area
- Repeats your existing signal
- Best for small dead zones or one far room
Mesh WiFi System
- More expensive, but better coverage
- Comes with 2–3 units (router + satellites)
- All work together as a single network
- Ideal for:
- Multi-story homes
- Thick walls
- Large apartments/houses
If your home is big or very divided, mesh systems usually give the most stable and consistent WiFi speeds.
10. Restart and Reset (The Right Way)
Sometimes, simple resets really do help.
Restarting:
- Turn off the modem and router.
- Wait 30 seconds.
- Turn the modem back on, wait until all lights are stable.
- Then turn on the router.
Factory reset (only if needed):
- Use a small pin to press the reset button on the router for about 10 seconds.
- This wipes all settings, so:
- Only do this if your router is acting very strange or you forgot the password.
- You’ll need to set up your WiFi name and password again.
11. When to Upgrade Your Router or Contact Your Provider
Sometimes, the simplest fix is: your hardware or plan is just too old.
Consider:
- Router age: If it’s over 4–5 years old, it may not support modern WiFi standards or higher speeds.
- Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) routers handle many devices better and can offer faster, more stable connections.
- Internet plan: If you’ve added more devices and started streaming more, your old plan may not be enough.
Talk to your provider if:
- Speed tests are always far below what you pay for (even with a cable connected directly to the modem).
- Your connection drops often.
- Neighbors on the same provider get much better performance.
Ask if:
- There are outages or issues in your area.
- You need a new modem.
- You can upgrade to a faster plan at a reasonable cost.
Quick Checklist: Easy WiFi Speed Boosts You Can Do Today
- Move your router to a central, high, open location
- Connect main devices to the 5 GHz (or 6 GHz) band
- Change WiFi channel if you live in a crowded area
- Update router firmware and device software
- Set a strong password and remove unknown devices
- Reduce heavy streaming or downloads during important calls
- Turn on QoS to prioritize work and video calls
- Consider a WiFi extender or mesh system for weak rooms
Try these in order—often, a combination of better placement, updated settings, and network cleanup is enough to make your WiFi feel brand new.

